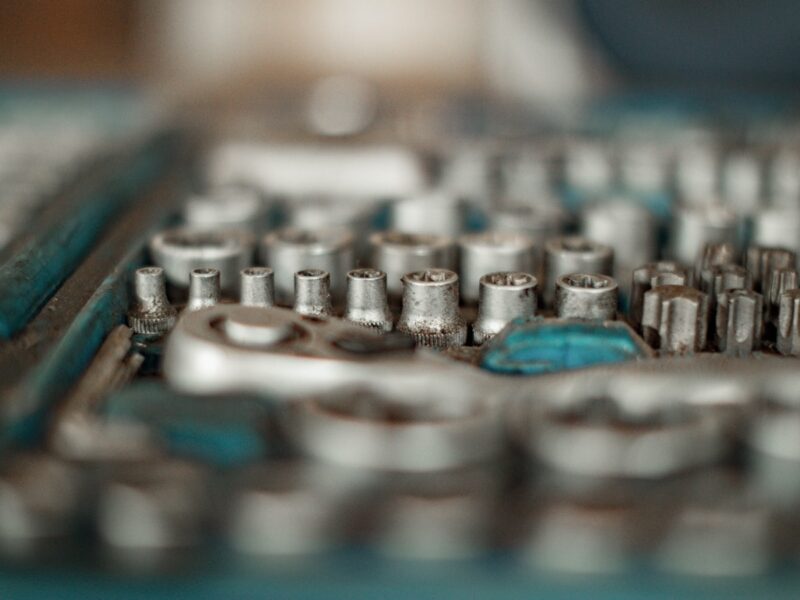
The sensor network is designed so the chips could presumably also be implanted into the body or constructed-in into wearable devices. Every submillimeter-sized silicon sensor mimics how neurons within the mind talk by spikes of electrical process. Credit ranking: Reduce Dentamaro/Brown University
This innovative methodology furthers the enchancment of wi-fi sensor expertise and opens the door to the aptitude employ of expansive numbers of unobtrusive sensors in implantable and wearable biomedical microdevices within the future.
Runt chips could presumably equal a big breakthrough for a team of scientists led by Brown University engineers.
Writing in Nature Electronics, the analysis team describes a unusual methodology for a wi-fi verbal replace network that could presumably efficiently transmit, receive, and decode recordsdata from hundreds of microelectronic chips that are every no increased than a grain of salt.
The sensor network is designed so the chips could presumably also be implanted into the body or constructed-in into wearable devices. Every submillimeter-sized silicon sensor mimics how neurons within the mind talk by spikes of electrical process. The sensors detect specific events as spikes and then transmit that recordsdata wirelessly in steady-time the employ of radio waves, saving every vitality and bandwidth.
Efficient Details Transmission Impressed by the Mind
“Our mind works in a in reality sparse contrivance,” mentioned Jihun Lee, a postdoctoral researcher at Brown and search for lead creator. “Neurons create now not fire your whole time. They compress recordsdata and fire carefully so that they are very efficient. We’re mimicking that building right here in our wi-fi telecommunication methodology. The sensors wouldn’t be sending out recordsdata your whole time — they’d beautiful be sending connected recordsdata as wished as fast bursts of electrical spikes, and they also could presumably be ready to create so independently of the numerous sensors and with out coordinating with a central receiver. By doing this, we would prepare to place heaps of vitality and steer away from flooding our central receiver hub with much less important recordsdata.”
This radiofrequency transmission design also makes the plot scalable and tackles a usual scenario with present sensor verbal replace networks: all of them could presumably need to be perfectly synced to work properly.
Writing in Nature Electronics, the analysis team describes a unusual methodology for a wi-fi verbal replace network that could presumably efficiently transmit, receive, and decode recordsdata from hundreds of microelectronic chips that are every no increased than a grain of salt. Credit ranking: Reduce Dentamaro/Brown University
The researchers dispute the work marks a important step forward in tidy-scale wi-fi sensor expertise and can sooner or later succor form how scientists internet and account for recordsdata from these minute silicon devices, severely since digital sensors have change into ubiquitous as a results of in vogue expertise.
“We’re residing in a world of sensors,” mentioned Arto Nurmikko, a professor in Brown’s College of Engineering and the hunt for’s senior creator. “They are throughout the contrivance. They’re absolutely in our automobiles, they are in so many areas of work and extra and extra getting into into our homes. The most annoying atmosphere for these sensors will continuously be inner the human body.”
Applications in Biomedical Sensors
That’s why the researchers imagine the plot can succor lay the foundation for the next generation of implantable and wearable biomedical sensors. There is a rising want in medication for microdevices that are efficient, unobtrusive, and unnoticeable but that also aim as section of a tidy ensembles to design physiological process within the course of a entire space of hobby.
“Here’s a milestone by truly creating this form of spike-basically based wi-fi microsensor,” Lee mentioned. “If we proceed to employ outmoded systems, we are succesful of now not internet the excessive channel recordsdata these features would require in all these subsequent-generation systems.”
The events the sensors name and transmit could presumably also be specific occurrences such as adjustments within the atmosphere they are monitoring, including temperature fluctuations or the presence of obvious substances.
The sensors are ready to employ as minute vitality as they invent because external transceivers provide wi-fi vitality to the sensors as they transmit their recordsdata — meaning they beautiful could presumably need to be inner fluctuate of the vitality waves despatched out by the transceiver to internet a charge. This capacity to aim with out needing to be plugged into a vitality provide or battery makes them convenient and versatile to be used in quite a lot of different scenarios.
The team designed and simulated the advanced electronics on a pc and has worked by several fabrication iterations to create the sensors. The work builds on outdated analysis from Nurmikko’s lab at Brown that launched a unique form of neural interface plot called “neurograins.” This methodology primitive a coordinated network of dinky wi-fi sensors to file and stimulate mind process.
“These chips are pretty refined as diminutive microelectronic devices, and it took us a while to internet right here,” mentioned Nurmikko, who will possible be affiliated with Brown’s Carney Institute for Mind Science. “The amount of work and effort that’s required in customizing the several various features in manipulating the digital nature of these sensors — that being basically squeezed to a a part of a millimeter space of silicon — is now not trivial.”
Constructing and Future Instructions
The researchers demonstrated the effectivity of their plot as properly as beautiful how a lot it will potentially be scaled up. They examined the plot the employ of 78 sensors within the lab and chanced on they were ready to acquire and ship recordsdata with few errors, even when the sensors were transmitting at various instances. Through simulations, they were ready to conceal decode recordsdata aloof from the brains of primates the employ of about 8,000 hypothetically implanted sensors.
The researchers dispute the next steps encompass optimizing the plot for reduced vitality consumption and exploring broader features beyond neurotechnology.
“The present work provides a technique we are succesful of further gain on,” Lee mentioned.
Reference: “An asynchronous wi-fi network for capturing event-driven recordsdata from tidy populations of self sustaining sensors” by Jihun Lee, Ah-Hyoung Lee, Vincent Leung, Farah Laiwalla, Miguel Angel Lopez-Gordo, Lawrence Larson and Arto Nurmikko, 19 March 2024, Nature Electronics.
DOI: 10.1038/s41928-024-01134-y
The quest for was funded by the Nationwide Institutes of Well being.